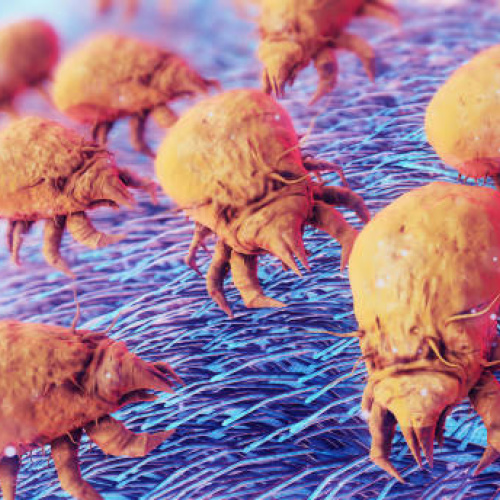
Dust mites are microscopic microorganisms that thrive in warm, moist atmospheres. They are typically found in homes, specifically in bedding, carpetings, and upholstered furnishings. With a brief life process of concerning 30 to 90 days, female allergen can lay between 80 to 100 eggs per cycle, causing fast population development. Their key food resource is the dead skin cells dropped by people and pets daily. While they are harmless by themselves, their waste and body fragments can activate allergic reactions and respiratory issues, making them a major concern for several households.

Where Do Allergen Live?
Allergen choose environments where warmth and moisture are consistent. They flourish in places such as cushions, cushions, drapes, and soft home furnishings, where human and pet dander accumulates. Given that they take in wetness from the air instead of alcohol consumption water, high moisture levels urge their survival. Poor ventilation, excessive dirt accumulation, and chaotic rooms provide the perfect setting for allergen to multiply. Rooms are usually one of the most afflicted locations given that they provide the best combination of heat, dampness, and a plentiful food supply.
Health Consequences of Dust Mites
Although allergen do not bite or spread illness, they are an usual reason for allergies and asthma. Their feces and body fragments include healthy proteins that can set off allergies when inhaled. Symptoms of dust mite allergies consist of sneezing, runny nose, scratchy or watery eyes, and skin inflammation. People with bronchial asthma may experience aggravated symptoms such as difficulty breathing and breast tightness. Long-term exposure to dust mite allergens can additionally add to persistent respiratory system conditions, making it vital to manage their visibility in interior areas.
Exactly How to Minimize Dust Mite Infestations
Controlling Dust mite begins with lowering interior humidity levels, as they flourish in moist settings. Making use of dehumidifiers or cooling can help preserve humidity below 50%, making it harder for them to survive. Washing bedding, pillow cases, and drapes in warm water weekly is an efficient way to eliminate dust mites and eliminate irritants. Regular vacuuming with HEPA filters can help in reducing their populace in carpetings and furnishings. Furthermore, using allergen-proof bed mattress and pillow covers can stop dust mites from collecting in bed linens, developing a much healthier resting environment.
Conclusion
Dust mites are undetectable yet widespread house insects that can create considerable illness, particularly for allergic reaction and bronchial asthma victims. Their fast reproduction cycle and reliance on shed skin cells make them tough to remove totally. By maintaining a clean, well-ventilated home and reducing moisture degrees, it is feasible to minimize dust mite infestations and their adverse results. Taking these preventive measures can bring about a much healthier and extra comfy living space.